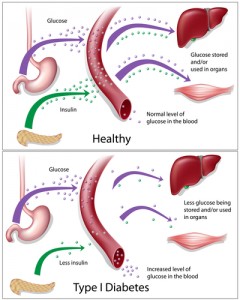
Type 1 diabetes was originally known as juvenile diabetes, even though this serious medical condition can occur in both children and adults; males and females. Your body needs to produce enough insulin to transform sugars and nutrients into energy. If your body does not create any insulin, you have Type 1 diabetes.
Type 1 Diabetes Statistics
There are approximately 25.8 million Americans who have diabetes, and 7 million people are undiagnosed. Of the millions of individuals diagnosed with diabetes, only 5 percent of them will have Type 1 diabetes.
Causes of Type 1 Diabetes
According to the Mayo Clinic, the exact cause of Type 1 diabetes is unknown. A common cause of diabetes is the immune system. Your immune system has the responsibility to fight off viruses and harmful types of bacteria. When your immune system does this, it also unintentionally destroys your insulin. When your body is exposed to certain viruses, those infections could lead to diabetes Type 1.
Even though Type 1 diabetes is hereditary, most individuals who are diagnosed with the disease have no family history of the illness.
Risks
There are risk factors that increase your chances of developing this type of diabetes. Some of those risk factors include:
- Viral Exposure
- Dietary Factors
- Early Vitamin D
- Geography
- Genetics
- Family History of Type 1 diabetes
Other risk factors are:
- Being born with jaundice.
- Having a respiratory infection following birth.
- Your mother had preeclampsia during her pregnancy.
- Your mother was under the age of 25 when she gave birth to you.
Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes
If you have any symptoms of Type 1 diabetes, those symptoms will develop quite early. When your blood sugars rise above your normal levels, you can notice symptoms as early as a few days or weeks. The most common symptoms of Type 1 diabetes are:
- Fatigue
- Inability to Heal
- Increased Thirst
- Extreme Hunger
- Drastic Weight Loss
- Frequent Urination
- Blurred Vision
Diagnosis
If you have any of the symptoms associated with Type 1 diabetes, you should consult with a medical expert immediately. Failing to diagnose and treat diabetes can lead to strokes, blindness, and death. Only a doctor can diagnose you with diabetes. The 3 tests for Type 1 diabetes are the A1C Test, the Random Blood Sugar test, and the Fasting Blood Sugar test. Do not assume you have the disease unless a doctor has performed 1 of the 3 tests on you. Sometimes those tests will be conducted more than once to ensure you receive accurate results.
To read more about tests for Type 1 diabetes, please click here.
Preventing Type 1 Diabetes
There are no precautions you can take to prevent Type 1 diabetes. Researchers are developing new methods to stop the disease from progressing once it is caught early-on. So far there are only trials available, which your doctor will be able to recommend or approve you for. Remember that there are no guarantees with these clinical trials, and there could be serious risks involved with the trials.
Complications
If you have developed Type 1 diabetes, the complications could have a negative affect on your major body organs. Those organs include:
- Kidneys
- Blood Vessels
- Heart
- Eyes
- Nerves
You will have to maintain normal blood sugar levels at all times, which can be extremely frustrating. If you fail to do so, the complications can be severe and even lead to death.
Treatment for Type 1 Diabetes
If you have been diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes, there are different treatment options available for you. Most diabetics have to take insulin if they have Type 1 diabetes. Insulin therapy is necessary in order for you to maintain healthy blood sugar levels. You have the option to inject insulin into your body through a pen, pump, syringe, or needle.
You will need to monitor your blood sugar levels throughout the day. You should eat healthy meals and snacks if you have Type 1 diabetes, in addition to exercising on a regular basis. Your mission is to maintain a healthy weight.
Living with Type 1 Diabetes
There is no reversal for Type 1 diabetes. If you have been diagnosed with this medical condition, you will need to exert a lot of time and energy in order to maintain good health. You do not want your emotions to harm your body both directly and indirectly. To avoid these types of risks, such as depression and anxiety, you need to create a healthy lifestyle.
Consult with your doctor about your available treatment options, in addition to counseling and support groups that are available near your home. Talking with others who suffer from Type 1 diabetes – or those who have a family member with the disease – could be extremely helpful. It is healthy for you to discuss your treatment options, experiences, and other topics with individuals who know what you are going through.
References
“Diabetes Basics.” American Diabetes Association. Retrieved from http://www.diabetes.org/diabetes-basics/type-1/. Accessed on August 16, 2013.
 Unanswered Questions?
Call Our Helpful Staff at
866 418 8004
Unanswered Questions?
Call Our Helpful Staff at
866 418 8004